Innovations and Considerations in Dental Implant Technology
Dental implants, a groundbreaking advancement in dental restoration, are primarily composed of carbon materials, metals, and ceramics. Metals, known for their mechanical properties, have been the choice material for early implant developments and continue to be widely used under strict biocompatibility standards.
1. The Evolution of Implant Procedures Implant dentistry has become a standard treatment for tooth loss, continuously evolving in simplicity, safety, and reliability. Patient consent and regular check-ups are vital. Successful implantation requires good overall health, absence of severe diseases, and healthy oral conditions, including adequate bone density and volume in the toothless area, which can be achieved through specialized surgical interventions if needed.
2. The Principle of Dental Implantation Dental implants are anchored in the alveolar bone, necessitating comprehensive and tight bone encapsulation around the implant. Like planting a tree in soil, sufficient bone is crucial to support the implant. Tooth loss often leads to bone remodeling and resorption, making pre-implantation evaluation essential.
3. Titanium: The Preferred Metal for Implants Titanium and its alloys, favored for their biocompatibility and mechanical properties, are the most popular metals used in dental implants. Their low density, high strength, and elastic modulus closely resembling bone tissue grant them ideal biomechanical compatibility. Titanium implants are highly successful and recommended by international implant associations.
4. Pre-implant Considerations and Selection of Clinics The overall health of a patient and specific local conditions of the implant site are critical for implant success. Women are advised to avoid implantation procedures during menstruation, and dietary precautions are necessary. Choosing a reputable clinic for the procedure is crucial.
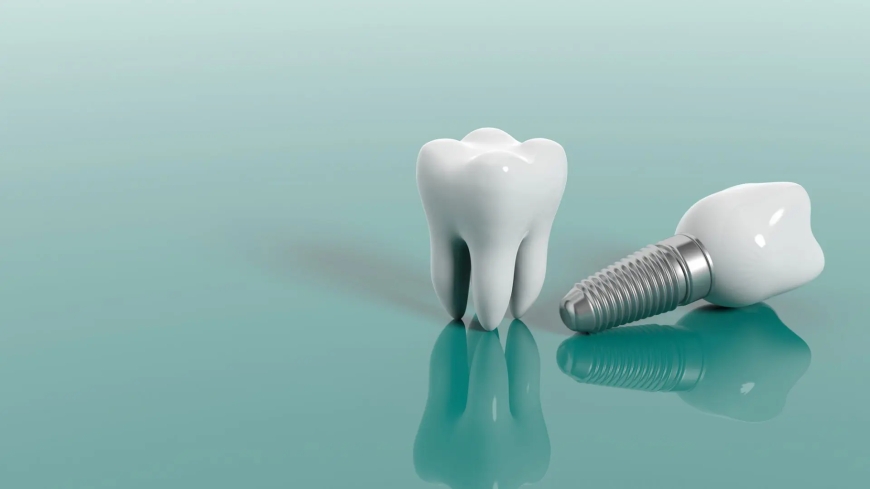
5. Components of a Dental Implant A dental implant typically comprises an implant body, threads, and an artificial crown. The implant body, resembling a screw or pillar, is made of titanium alloy and inserted into the jawbone, acting as a substitute for the natural tooth root. It integrates with the bone to provide support and stability.
6. The Role of Threads in Implants Threads are connectors between the implant body and the crown or prosthetics, usually made of titanium alloy or ceramic. Located above the gum line, they secure the artificial crown, contributing to the aesthetic gum contour and overall implant structure.
7. Artificial Crowns in Dental Implants The artificial crown, the visible part of the implant, mimics the natural tooth crown. Made from ceramic or metal alloys, it offers both aesthetic appeal and functional chewing capability. It is fixed to the thread, creating a natural appearance and seamless integration with surrounding teeth.
8. Customizing Dental Implant Treatments Apart from these components, dental implants involve auxiliary parts like soft tissue mimetics, thread switches, and repositioners. Material and component choices vary based on individual needs, doctor preferences, and aesthetic and functional requirements. Customized treatment plans are formulated after thorough oral examinations, ensuring tailored implant solutions for each patient.
What's Your Reaction?




























:quality(85):upscale()/2024/01/25/878/n/1922153/f94f61ec65b2bf18018990.47538761_.jpg)

:quality(85):upscale()/2024/01/26/759/n/29590734/b7f6660b65b3e8460d7196.77057039_.jpg)
:quality(85):upscale()/2024/01/27/741/n/1922153/8d43a26665b533b214de01.38307153_.jpg)











